What are Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs)
Gain essential insights on Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) at TradeFXP blogs. Understand their role, benefits, risks, and how they influence your investment portfolio.
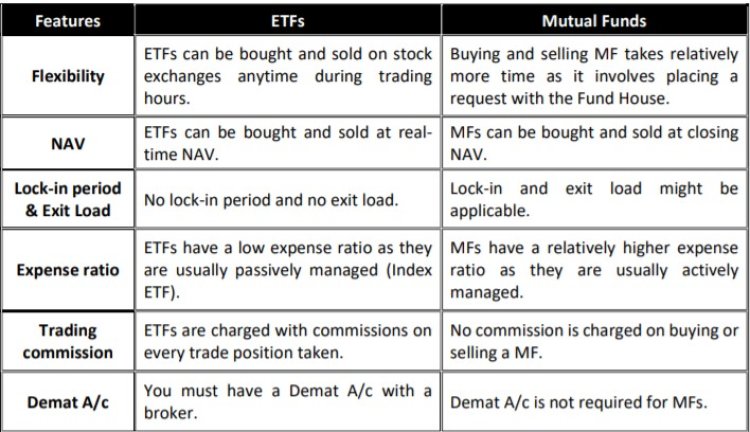
Do you know what Exchange-Traded Funds are (ETFs)?
The basics of Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
We live in an ever-changing world. Everything happens in a flash. Our consumption style evolved along with our lifestyle. There's no news that we love 2-in-1 products or services these days.
There is nothing more we can ask for than a product that is less expensive and serves multiple purposes. Whether you're looking for minty toothpaste, sunscreen moisturizer, convertible bags, sofa beds, or Bluetooth-enabled hoodies, we have it all. There is no end to the list.
Our financial market wasn't left out either. An Exchange Traded Fund, or ETF, jumped on this trend.
Combining mutual funds and stocks offers the best of both worlds. We'll explore what makes ETFs so appealing in the coming years since they've gained popularity for all the right reasons.
How do Exchange-Traded Funds work (ETFs)?
The exchange-traded fund (ETF) invests in a variety of financial assets and is traded on a stock exchange. Stocks, bonds, currencies, commodities, or currencies can be held by ETFs.
An ETF is traded on a stock exchange, just like any other listed stock. Among the various types of ETFs are Index ETFs, Equity ETFs, Gold ETFs, Debt ETFs, and even International ETFs.
Market movements affect the NAV of an ETF. ETFs are flexible enough to be traded short-term or held long-term. During regular trading hours, you are free to purchase as many units as you want.
Considerations
a) Risk
Diversifying your portfolio with ETFs is a good idea. A mutual fund or stock is riskier than owning a stock.
Market volatility and higher risks are common in short-term (less than one year) investments. That requires a deeper understanding of stock markets.
b) The cost of trading
ETFs can be traded on stock exchanges like stocks. When you trade ETFs, you incur trading costs or charges.
As a result, if you frequently trade ETFs as you do stocks, it may not be as cost-effective as trading stocks. Liquidity concerns should also be taken into account when selecting an ETF.
c) Dividends/ Interests
Dividends/interest earned on assets is required to be paid by ETF issuers to their investors. In addition to distributing these earnings in cash, the issuer can also reinvest them in more ETF units.
It is up to the issuer to make the decision. Investing in ETFs requires knowing what they offer.
d) Tax
As of the financial year 2020-21, dividend distribution tax is calculated based on your income tax slab rate. ETFs fall into various categories for tax purposes.
Taxes on equity ETFs are the same as those on equity mutual funds. Gold ETFs, International ETFs, and Debt ETFs are taxed as debt mutual funds.
What type of investor should I be?
Over the past few years, ETF demand has steadily increased. Passively managed ETFs might make a good addition to your portfolio.
Your portfolio can be diversified and the risk factor minimized. As such, this instrument is suitable for investors who have a long-term investment horizon and a low appetite for risk. Young investors will also find it a good low-cost option.
In summary
It depends on your financial goals and risk tolerance, whether you invest in an ETF long-term or short-term.
Identifying one's financial goals and risk appetite is crucial to making an informed investment decision. Investors have varying risk appetites and investment horizons, which are accommodated by different ETF categories.
To achieve your investment goal optimally, you should weigh all available options. A professional portfolio manager can help you diversify your portfolio with ETFs.



 admin
admin